In the ever-expanding world of fermented beverages, the terms “Mother of Vinegar” and “SCOBY” often surface, sparking curiosity among enthusiasts. Let’s delve into the intricacies of these components, unraveling the differences that set them apart.
Understanding Mother of Vinegar
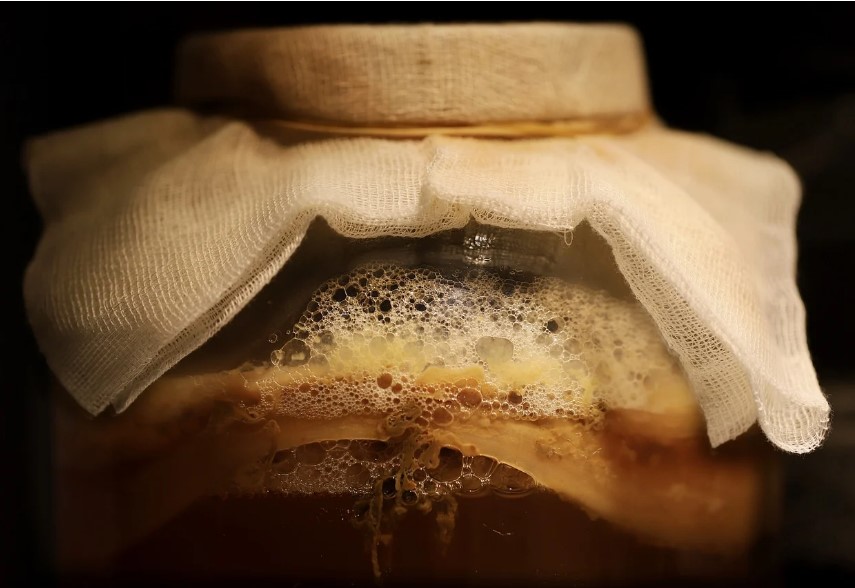
Mother of Vinegar, an enigmatic term for many, is a fascinating entity that plays a pivotal role in the vinegar-making process. Contrary to popular belief, it is not a maternal figure but rather a collection of acetic acid bacteria and cellulose strands. This gelatinous mass forms naturally during the fermentation of alcoholic liquids, transforming them into vinegar.
The Birth of Mother of Vinegar
When alcohol undergoes fermentation, the acetic acid bacteria in the environment collaborate to convert ethanol into acetic acid. This transformation results in the creation of Mother of Vinegar, a complex structure with a slightly tangy taste and a plethora of health benefits.
Demystifying SCOBY: Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast
In the realm of kombucha and fermented teas, SCOBY takes center stage. An acronym for Symbiotic Culture of Bacteria and Yeast, SCOBY represents a harmonious alliance that brings forth the magic of fermentation.
The Dual Nature of SCOBY
Unlike Mother of Vinegar, SCOBY consists of both bacteria and yeast, working in tandem to ferment sweet tea into the effervescent elixir known as kombucha. The yeast component ferments sugars into alcohol, while the bacteria convert the alcohol into acetic acid.
Key Differences: Mother of Vinegar vs. SCOBY
Composition
Mother of Vinegar predominantly comprises acetic acid bacteria and cellulose strands, forming a distinct gelatinous mass. On the other hand, SCOBY boasts a more diverse composition, featuring both bacteria and yeast, creating a symbiotic relationship crucial for kombucha production.
Culinary Applications
While Mother of Vinegar contributes to the tangy flavor profile of vinegar-based dishes, SCOBY opens up a world of possibilities in the realm of kombucha and fermented teas. Its influence extends beyond flavor, impacting the effervescence and health benefits of the final product.
Fermentation Process
Mother of Vinegar arises naturally during the fermentation of alcoholic liquids, primarily wine or cider. In contrast, SCOBY is intentionally introduced into sweet tea to initiate the fermentation process, converting sugars into alcohol and ultimately into kombucha.
Choosing the Right Component for Your Culinary Adventures
Mother of Vinegar in Culinary Delights
If your culinary journey leans towards the realm of vinegars and dressings, embracing Mother of Vinegar can elevate your creations. Its tangy undertones and natural probiotic properties make it a versatile addition to salad dressings, marinades, and pickles.
Embracing SCOBY for Kombucha Crafting
For those intrigued by the world of fermented teas and health elixirs, SCOBY is the hero of your journey. Start your kombucha crafting adventure by introducing this symbiotic culture into sweet tea, witnessing the magical transformation unfold as it ferments into a bubbly, probiotic-rich beverage.
Conclusion: Embracing Fermentation Wonders
both Mother of Vinegar and SCOBY contribute to the captivating world of fermentation, each with its unique characteristics and applications. Whether you embark on vinegar-making endeavors or delve into the art of kombucha crafting, understanding these components enhances your culinary prowess.









